API Tool Calling: 6 Effective Steps using Goldfinch AI
December 2, 2025TL;DR
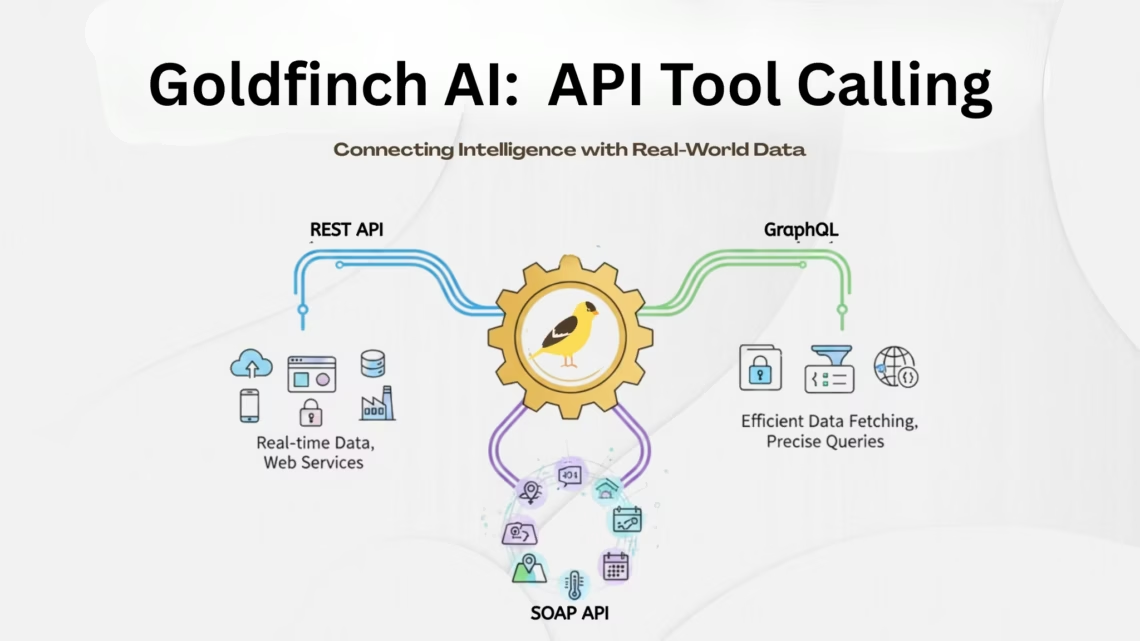
The API Tool Calling Tool in Goldfinch AI enables AI agents to securely connect to external REST APIs, fetch real-time data, and convert technical API responses into clear, human-readable answers within a single workflow.
It removes the need for manual coding or custom integrations by allowing users to configure API calls directly through a no-code UI. The tool supports single-step and multi-step workflows, dynamic parameter mapping, multiple authentication methods (No Auth, Basic Auth, OAuth 2.0), response filtering, and optional LLM-based summarization.
By combining API execution and AI interpretation, Goldfinch makes real-time data access easier, faster, and more scalable—especially for automation, analytics, and conversational AI use cases. It is best suited for teams that need reliable external data and AI-driven insights without heavy engineering effort.
What is the API Tool Calling Tool in Goldfinch AI?
The API Tool Calling Tool allows Goldfinch AI agents to connect to external REST APIs, retrieve real-time data, and present the results in clear, human-readable language.
It acts as a bridge between Goldfinch AI and third-party systems, enabling data retrieval, processing, and summarization within a single AI workflow.
Why is the API Tool Calling Tool needed?
It eliminates the need for manual API integrations by letting users define and execute API calls directly from the Goldfinch interface.
This reduces engineering effort while enabling real-time data access for automation, analytics, and conversational AI use cases.
How does the API Tool Calling Tool work?
The tool sends a configured API request, receives the response, and either returns it directly or processes it through an LLM for natural-language output.
How it works (steps):
-
User defines the API endpoint, method, and parameters in the Goldfinch UI
-
Goldfinch executes the API call securely
-
The response is filtered and validated
-
An LLM optionally converts the response into a conversational answer
What types of workflows does it support?
It supports both single-step and multi-step API workflows.
When to use multi-step workflows:
-
When one API response is required as input for another API or an LLM
-
Example: Weather API → LLM summary for end users
Key Features
- Multi-step API Workflow – Supports sequential API calls, where the output of one step can be passed as input to another (e.g, API -> LLM).
- Dynamic Parameter Mapping – Automatically replaces placeholders such as (%goldfinch_user_question%} with real-time user input.
- Flexible Authentication – Supports multiple authentication types including No Auth, Basic Auth, Token-based Auth, etc.
- Configurable Headers & Body – Allows users to define custom headers, body formats (JSON, form-data), and query parameters.
- Response Filtering – Enables selective extraction of response data using filter expressions like [‘choices’][0] [‘message’] [‘content’].
- LLM Integration – Integrates with large language models to interpret and present API responses in natural language.
API Calling Workflow
- External API Call:
Sends a request to the configured endpoint with user-defined parameters, headers, and body. - Response Processing:
The response is either returned directly to the user or processed further by Goldfinch AI to generate a natural-language summary.
Authentication Types Supported
| Authentication Type | Description | Example Usage | Security Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| No Auth | No credentials required. Used for open APIs. | Weather API | Low |
| Basic Auth | Username and password encoded in Base64 and sent in the Authorization header. | Internal APIs | Medium |
| OAuth 2.0 (Refresh Token) | Token-based authentication. Uses Access Token and Refresh Token to securely authorize API calls. | Enterprise APIs (Google, Salesforce) | High |
What is the Goldfinch API Calling UI?
Answer: It is a configuration interface that allows users to define all aspects of an API call without writing code.
Sections and purpose:
-
Params: Query strings and dynamic inputs
-
Auth: Authentication type and credentials
-
Headers: Metadata such as content type
-
Body: Payload for POST/PUT requests
-
Schema: Response validation and filtering
-
Settings: Execution controls like HITL and memory
Params (Parameters)
Purpose: Used to send additional data along with the API request — often as query strings or URL parameters.
Fields commonly provided:
- query: Contains the dynamic user input (e.g., city name, ID, keyword).
- access_key: Used for authorization in public APIs (hidden for security).
Example:
{
"query": "{%goldfinch_user_question%}",
"access_key": "************"
}
Auth (Authentication)
Purpose: Defines the type of authentication used to access the API endpoint.
Options available:
- No Auth: For public APIs.
- Basic Auth: Enter username and password.
- OAuth 2.0: Configure Access Token and Refresh Token fields for secure authentication.
Headers
Purpose: Used to send additional metadata about the request, such as content type or authorization credentials.
Example:
{
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
Body
Purpose: Used to send data to the server (especially in POST, PUT, or PATCH methods).
Supported Formats:
- JSON Format
- Text Format
Example:
{
"city": "Bengaluru",
"units": "metric"
}
Schema
Purpose: Defines how the response from the API should be handled, filtered, and validated.
Fields included:
- Response Type
- Filter Response
- Parameters
- Required Payload
- Expected Payload
Settings
Key Fields:
- HITL (Human In The Loop)
- API HITL
- STM (Short-Term Memory)
Configuration steps for API Calling
The API Calling Tool in Goldfinch AI allows users to configure and connect to APIs that use different authentication methods.
Configuration for “No Auth”
Use Case: Fetching public data from a Weather API.
API reference: https://openweathermap.org/api
- Open the API Calling tool in Goldfinch.
- Select No Auth.
- Add Params: query & access_key.
- Set Header: Content-Type: application/json.
- Set Method: GET.
- Leave Body empty.
- Settings: HITL=0, STM=1.
Configuration for “Basic Auth”
Use Case: Accessing a User Details API requiring username/password.
Example: Access a User Details API. Learn
Configuration for “OAuth 2.0 (with Refresh Token)”
Use Case: Retrieving data from a testing API that uses token-based authentication.
Example: Token-based testing API. Learn
What security measures are in place?
Answer: The API Tool is designed with enterprise-grade security controls.
Security features:
-
No local credential storage
-
Role-based access control
-
OAuth token rotation
-
Controlled API execution environment
What advantages does Goldfinch offer over other API tools?
Answer: Goldfinch combines API execution and AI interpretation in one unified workflow.
Key advantages:
-
No separate automation or middleware required
-
Faster setup compared to traditional integration platforms
-
AI-ready outputs by default
-
Designed for automation at scale
Who is this tool best suited for?
Answer: Teams that need real-time data access, automation, and AI-driven insights without complex engineering work.
Common users:
-
Product teams
-
Automation engineers
-
AI solution architects
-
Enterprise operations teams
Conclusion
The API Calling Tool in Goldfinch AI provides a secure, configurable, and intelligent way to interact with external APIs. By combining robust API handling with AI-driven data interpretation, it allows users to access real-world information and insights seamlessly – turning complex technical operations into smooth, human-like interactions.
For more details, visit eZintegrations: https://ezintegrations.ai/
FAQ
A tool in Goldfinch AI that lets agents call external REST APIs and return responses in natural language.
It sends requests to configured APIs, processes the response, and presents it conversationally to the user.
It supports No Auth, Basic Auth, and OAuth 2.0 with Refresh Token.
Yes, it can chain multiple API calls and pass outputs between steps.
It dynamically maps placeholders like {%goldfinch_user_question%} to real user input.
Users who need real-time external data retrieval, automation, and AI-driven interpretation within one workflow.